A blood glucose test, which measures the amounts of sugar in the blood, is commonly used to make a diagnosis. Prediabetes is a condition in which the fasting blood sugar level is high but not to the point of diabetes. Prediabetes is a condition in which people have increased fasting glucose levels on multiple occasions, increasing their chance of acquiring full-blown diabetes.
Types of Diabetes:
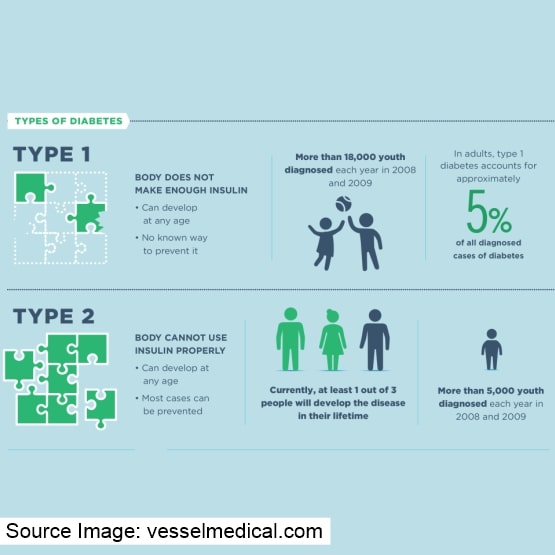
Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are the two most common types of diabetes. Both forms of diabetes can strike at any age, but Type 1 diabetes is more common in children.
Type 1 Diabetes
People with Type 1 diabetes are unable to use glucose (the body's primary sugar) for energy. This happens because their bodies have stopped producing the hormone insulin. Normally, the amount of glucose in our blood, also known as blood sugar, rises when we eat. The pancreas then releases insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin functions as a key to opening the doors of the body's cells, allowing glucose to enter and provide energy to the cells.The signs and symptoms of Type 1 diabetes in children usually develop quickly, and may include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination, possibly bed-wetting in a toilet-trained child
- Extreme hunger
- Unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue
- Irritability or behaviour changes
- Fruity-smelling breath
Risk factors
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes in children include:- Family history:
- Genetics:
- Certain viruses:
Anyone with a parent or siblings with Type 1 diabetes has a slightly increased risk of developing the condition.
Certain genes indicate an increased risk of Type 1 diabetes.
Exposure to various viruses may trigger the autoimmune destruction of the islet cells.

Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes affects how your child's body absorbs sugar and is a long-term condition. The illness causes sugar to build up in the blood, which can have dangerous long-term repercussions if not treated.Adults are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes. It was previously known as adult-onset diabetes. However, due to the obesity pandemic, Type 2 diabetes in youngsters is on the rise.
Type 2 diabetes in children can develop so slowly that no symptoms are visible. Occasionally, the disorder is discovered during a standard physical examination.
Other Symptoms that children with Diabetes may experience:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination:
- Fatigue:
- Blurry Vision:
- Darkening of Skin:
- Weight loss:
Excess sugar in your child's bloodstream draws fluid out of his or her tissues. As a result, your child may become thirsty, drinking and urinating more frequently than usual.
Your child may become exhausted due to a lack of sugar in his or her cells.
Fluid may be drained from your child's lenses if his or her blood sugar is too high. Your child may be unable to concentrate.
Certain parts of the skin, usually the neck and armpits, darken before Type 2 diabetes begins.
Without the energy that sugar supplies, muscle tissues and fat stores simply shrink. However, weight loss is less common in children with Type 2 diabetes than in children with Type 1 diabetes.
Risk factors
Even though they have identified risk factors, researchers don't completely understand why some children acquire Type 2 diabetes and others do not. However, it's clear that certain factors increase the risk, including:- Weight:
- Inactivity:
- Family history:
- Age and sex:
- Birth weight and gestational diabetes:
- Pre-term birth:
In children, being overweight is a substantial risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. The more fatty tissue a child has, particularly around the belly, the more insulin resistant their cells become.
A child's risk of Type 2 diabetes increases as he or she becomes less active. Physical activity helps your kid maintain a healthy weight, burns glucose for energy, and improves insulin sensitivity in his or her cells.
Children's risk of Type 2 diabetes increases if they have a parent or sibling with the disease.
Many children develop Type 2 diabetes in their early teens. Adolescent girls are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes than are adolescent boys.
Low birth weight and being born to a mother who had gestational diabetes during the pregnancy are both associated with a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Babies born prematurely — before 39 to 42 weeks gestation —have a greater risk of Type 2 diabetes.
Treatment

Type 1 diabetes can be treated with:
- Daily insulin injections
- Lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise
- Frequent blood glucose checking to monitor blood glucose levels
- Lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise
- Regular blood glucose testing
- Oral medication
- Insulin injections
What parents of children with diabetes can do

Although there is no cure for diabetes in children, it can be managed so that children with this condition can live normal lives. Blood sugar monitoring, treatment with insulin therapy (given as numerous injections per day or via an insulin pump), and keeping a balanced diet are all important aspects of managing the condition. Keeping blood sugars in a normal range is critical because it reduces the risk of long-term health concerns caused by poor diabetes management. In addition to a balanced diet, children can benefit from at least thirty minutes of exercise every day to help them manage their condition.
- To keep their blood sugars in a safe range, children with Type 1 diabetes must find the correct combination of diet, insulin, and activity. Understanding how different meals impact your child's blood sugar is beneficial.
- Staying active on a regular basis is an important part of diabetes therapy. Exercise helps the child to grow stronger. It also improves their mood and blood sugar levels. In fact, exercise improves insulin's efficiency. Diabetic children may and should exercise. Encourage your youngster to be active by setting a daily target of 60 minutes.
- With the advice of your child's doctor, plan a medical management strategy. Make a copy for their school. It should specify what the school should do in each circumstance. Events like parties and field trips may require additional planning. You and the staff at your child's school can work together to keep their diabetes under control.
- Seek out some support. Parents of diabetic children frequently feel alone. Due to the disease's uniqueness, families may not know anybody else who has diabetes. Join online diabetic support groups and Facebook communities for parents with children having diabetes to find out what others are going through.
